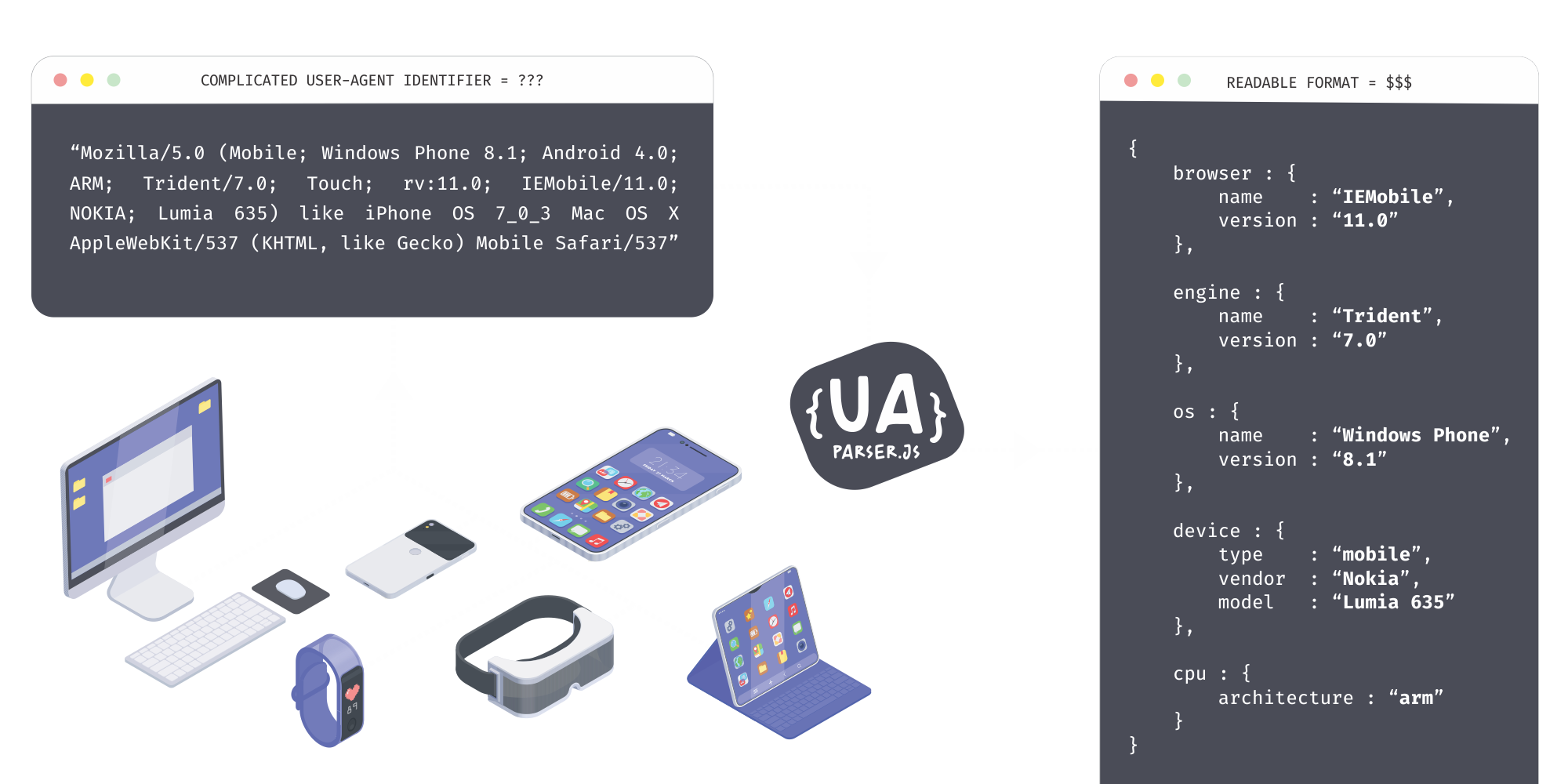
What your browser tells you:
What UAParser.js gives you:
Clean & Organized
Effortless, intuitive API delivering clear, consistent results.
Wide Coverage
Detects various devices, browsers, bots, apps, and more.
Lightweight & Fast
Keeps your bundle size compact and efficient.
Works Everywhere
Runs seamlessly across browsers and Node.js.
npm-Ready Package
Easily integrates into your existing workflow.
Lifetime Updates
Stay up-to-date with the ever-evolving trends.
"A great utility library to have when you're investigating what kind of users are visiting your website and how you can improve their UX. Supports most browsers out there."
Gabrijel Golubić
"Thanks to the awesome people who make life so much easier for developers.. The evolution of the internet has made it critical that we detect the user's device type accurately to make our apps function better and look better.".
The-Linguist
"I've been using your library for a long time and it totally rocks!".
Christian Rich
"Thank you for putting out this very useful library!".
Anuj Nijhawan
"For years, it has been appreciated as a valuable tool for web developers. Its ability to accurately parse user agent strings.. has made it an essential library for many of us.".
LogRocket
Case StudiesDiscover how leading companies use UAParser.js


































































Package Options
Pricing & comparison between editions
- Full features
- npm-ready
- Non-commercial usage rights
- Unlimited deployments
- 1 year support
- Lifetime updates
- Full features
- npm-ready
- Commercial usage rights
- 1 TLD per 1 license
- 1 year support
- Lifetime updates
- Full features
- npm-ready
- Commercial usage rights
- Unlimited deployments
- 1 year support
- Lifetime updates
| OSS Editions | Commercial Editions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| License | MIT (v1.0) | AGPL (>=v2.0) | PRO Personal | PRO Business | PRO Enterprise |
| Browser detection | |||||
| CPU detection | |||||
| Device detection | |||||
| Engine detection | |||||
| OS detection | |||||
| Bot detection | |||||
| AI Bot detection | |||||
| Extras (Apps, Libs, Emails, Media Players, etc) detection | |||||
| Enhanced detection result | |||||
| Client Hints support | |||||
| CommonJS support | |||||
| ES modules support | |||||
| TypeScript declarations | |||||
| npm module available | |||||
| Direct downloads available | |||||
| Allows commercial usage | |||||
| Permissive (non-copyleft) license | |||||
| No open-source obligations | |||||
| Unlimited end-products | |||||
| Unlimited deployments | |||||
| 1-year product support | |||||
| Lifetime updates | |||||
| Price (one-time fee) | FREE | FREE | $14 | $29 | $599 |
| GET NOW | |||||










